Overdose
When treating severe spasticity with Lioresal® Intrathecal (baclofen injection), it is mandatory that all patients, caregivers, and treating physicians receive adequate information regarding the risks of the mode of treatment. Importantly, instruction should be given on signs and symptoms of overdose, procedures to be followed in the event of an overdose, and proper home care of the pump and insertion site.1
What are the signs of Lioresal® Intrathecal overdose?
- Signs of overdose may appear suddenly or insidiously, and a massive overdose may present as coma. In most cases reported, coma was reversible without sequelae after drug was discontinued.
- Less sudden and/or less severe forms of overdose may present with signs of drowsiness, lightheadedness, dizziness, somnolence, respiratory depression, seizures, rostral progression of hypotonia, and loss of consciousness progressing to coma.1 Symptoms of Lioresal® Intrathecal overdose were reported in a sensitive adult patient after receiving a 25 mcg intrathecal bolus.1
Lioresal® Intrathecal overdose can mimic symptoms associated with sepsis, intracranial hemorrhage, hypoglycemia, Cushing’s triad, electrolyte imbalance, and seizure disorder. Overdose symptoms may include nausea and vomiting, dizziness, respiratory depression, hypothermia, rostral progression of hypotonia, and somnolence that have advanced to seizures and coma requiring ventilator support.2

Should overdose appear likely, the patient should be taken immediately to an emergency room or an intensive care unit for assessment. While there is no specific antidote for treating overdoses of Lioresal® Intrathecal, certain steps should ordinarily be undertaken1:
- Residual Lioresal® Intrathecal solution should be removed from the pump as soon as possible
- Patients with respiratory depression should be intubated if necessary until the drug is eliminated
- If lumbar puncture is not contraindicated, consideration should be given to withdrawing 30 to 40 mL of CSF to reduce the CSF baclofen concentration
Management of overdose starts with supportive measures, including maintenance of the airway, respiration, and circulation. Subsequent measures may include reduction or temporary interruption of ITB therapy by pump reprogramming. Draining of CSF from the catheter access port and sequential lumbar puncture or lumbar drains are optional. Patients with overdose must then be monitored closely for rebound withdrawal. Most patients recover completely with supportive care, fluids, and ventilator support.2
Emergent (Acute) Troubleshooting —Overdose2
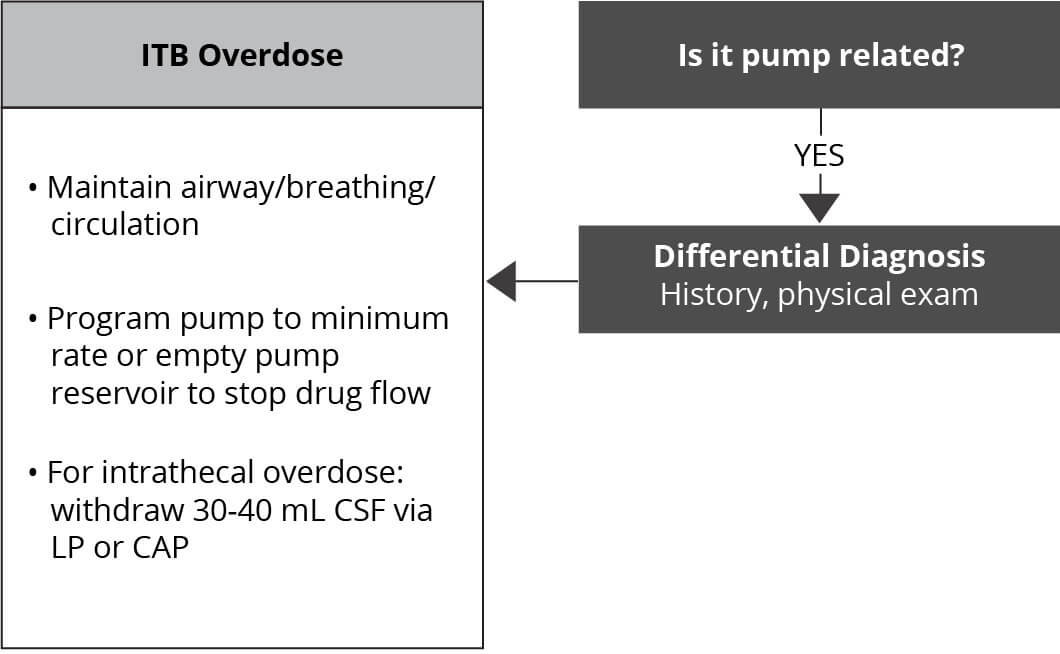
CAP, catheter access port; CSF, cerebral spinal fluid; LP, lumbar puncture.
Adapted from Reference 2: Saulino M, Anderson DJ, Doble J, et al. Best practices for Intrathecal baclofen therapy: troubleshooting. Neuromodulation. 2016;19(6):632-641.
- Lioresal® Intrathecal (baclofen injection) for intrathecal injection [prescribing information]. Saol Therapeutics, Roswell, Georgia; January 2019.
- Saulino M, Anderson DJ, Doble J, et al. Best practices for intrathecal baclofen therapy: troubleshooting. Neuromodulation. 2016;19(6):632-641.