Is Lioresal® Intrathecal Right for Your Patient?
When patients suffer from severe spasticity that interferes with their comfort, mobility, activity of daily living, or positioning, ITB Therapy℠ with Lioresal® Intrathecal (baclofen injection) provides another option for treatment beyond orals and injectables.1,2
Lioresal® Intrathecal is indicated for use in the management of severe spasticity.2
For many patients and physicians, treatment with Lioresal® Intrathecal is their management choice:
- 94% of patients with spasticity of cerebral origin and 97% of patients with spasticity of spinal origin have a positive screening test3
- 82% of patients said they would repeat the decision to receive ITB Therapy℠ with Lioresal® Intrathecal4
- 87% of physicians in one clinical study rated their overall satisfaction for patient outcomes as good or very good5
Before treatment with Lioresal® Intrathecal or implantation of a SynchroMed® II pump system can be considered, a patient must undergo a screening trial with Lioresal® Intrathecal.2 A screening trial consists of an injection of Lioresal® Intrathecal (a test dose) into the CSF under medical supervision to test how treatment affects spasticity.2
This screening trial can offer a glimpse of life with reduced spasticity and may uncover underlying function and whether it can be improved. After implantation of the SynchroMed® II pump, Lioresal® Intrathecal may decrease muscle tone and uncover muscle weakness that was not apparent before treatment. Rehabilitation may be used alongside Lioresal® Intrathecal treatment to retrain and strengthen the muscles that were affected by spasticity.6
If severe spasticity is due to spinal cord origin and is not controlled with oral baclofen or CNS side effects are not tolerable, ITB Therapy℠ with Lioresal® Intrathecal may be the right treatment choice.2 Patients with spasticity due to traumatic brain injury should wait at least one year after the injury before consideration of long-term ITB Therapy℠ with Lioresal® Intrathecal.2
Patients allergic to baclofen should not use Lioresal® Intrathecal.2 Patients with an active infection should not have a screening test or implant until the infection has been treated.2 Patients should not receive ITB therapy if their body size is too small to hold the implantable pump.2
ITB Therapy℠ with Lioresal® Intrathecal can only be implemented after a positive
screening trial.2
Is Lioresal® Intrathecal an Option for Patients Who Have Used Oral Baclofen?
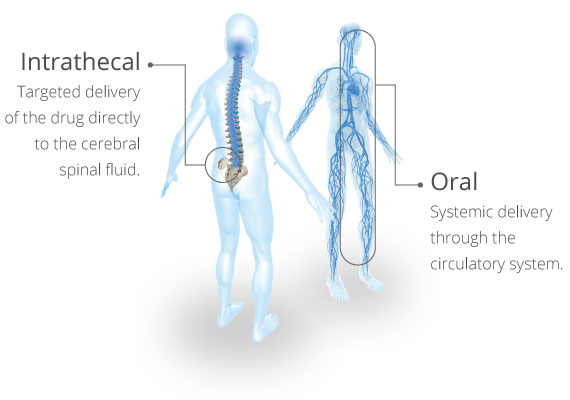
Many patients who currently use Lioresal® Intrathecal have previously used oral baclofen unsuccessfully or experienced intolerable side effects from taking oral baclofen.2 Baclofen tablets taken orally and Lioresal® Intrathecal both deliver baclofen, but by administering baclofen directly into the spinal fluid, Lioresal® Intrathecal can offer a more consistent reduction in severe spasticity at lower doses with potentially fewer side effects than are commonly associated with oral baclofen.1
The most frequent drug adverse events vary by indication but include: hypotonia (34.7%), somnolence (20.9%), headache (10.7%), convulsion (10.0%), dizziness (8.0%), urinary retention (8.0%), nausea (7.3%), and paresthesia (6.7%). Pump system component failures leading to pump stall, or dosing/programming errors may result in clinically significant overdose or underdose. Acute massive overdose may result in coma and may be life-threatening.
The most frequent and serious adverse events related to device and implant procedures are catheter dislodgement from the intrathecal space, catheter break/cut, and implant site infection including meningitis. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may cause patient injury, system damage, operational changes to the pump, and changes in flow rate.
- Saulino M, Ivanhoe CB, McGuire JR, et al. Best practices for intrathecal baclofen therapy: patient selection. Neuromodulation. 2016;19(6):607-615.
- Lioresal® Intrathecal (baclofen injection) for intrathecal injection [prescribing information]. Saol Therapeutics, Roswell, Georgia; January 2019.
- Gilmartin R, Bruce D, Storrs BB, et al. Intrathecal baclofen for management of spastic cerebral palsy: multicenter trial. J Child Neurol. 2000;15:71-77.
- Krach L, Nettleton A, Klempka B. Satisfaction of individuals treated long-term with continuous infusion of intrathecal baclofen by implanted programmable pump. Pediatr Rehabil. 2006;9(3):210-218.
- Guillaume D, Van Havenbergh A, Vloeberghs M, Vidal J, Roeste G. A clinical study of intrathecal baclofen using a programmable pump for intractable spasticity. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005;86(11):2165-2171.
- Boster AL, Bennett SE, Bilsky GS, et al. Best practices for intrathecal baclofen therapy: screening test. Neuromodulation. 2016;19(6):616-622.