ITB Therapy℠ With Lioresal® Intrathecal
Intrathecal baclofen therapy (ITB therapy) is delivered by the Medtronic SynchroMed® II Drug Infusion System, which consists of an implantable, programmable pump and an intrathecal catheter. Lioresal® Intrathecal (baclofen injection) is administered directly to the intrathecal space surrounding the spinal cord. This allows effective drug concentrations to reach the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), while the plasma remains relatively unaffected compared with oral administration.1-3
The use of ITB therapy has gained widespread use over the last several decades due to the advantages of targeted drug delivery with Lioresal® Intrathecal as well as innovations in infusion and pump technologies. The origin of this type of therapy can be traced to the turn of the 20th century (1898), first used by Bier for spinal anesthesia with intrathecal cocaine, after which the approach became a mainstay in anesthesiology. It took nearly 8 decades of use to transition from short-term use to applying this therapy to treat chronic conditions. ITB therapy was first used in spasticity in 1984 when Penn and Kroin described use of continuous intrathecal baclofen infusion for the reduction of spasticity following spinal cord injury.3,4 ITB Therapy℠ with Lioresal® Intrathecal has been commercially available in the U.S. since 1992 for severe spasticity of spinal origin and since 1996 for severe spasticity of cerebral origin.3 Thus, there is a long history of the safety and efficacy of ITB Therapy℠ with Lioresal® Intrathecal.
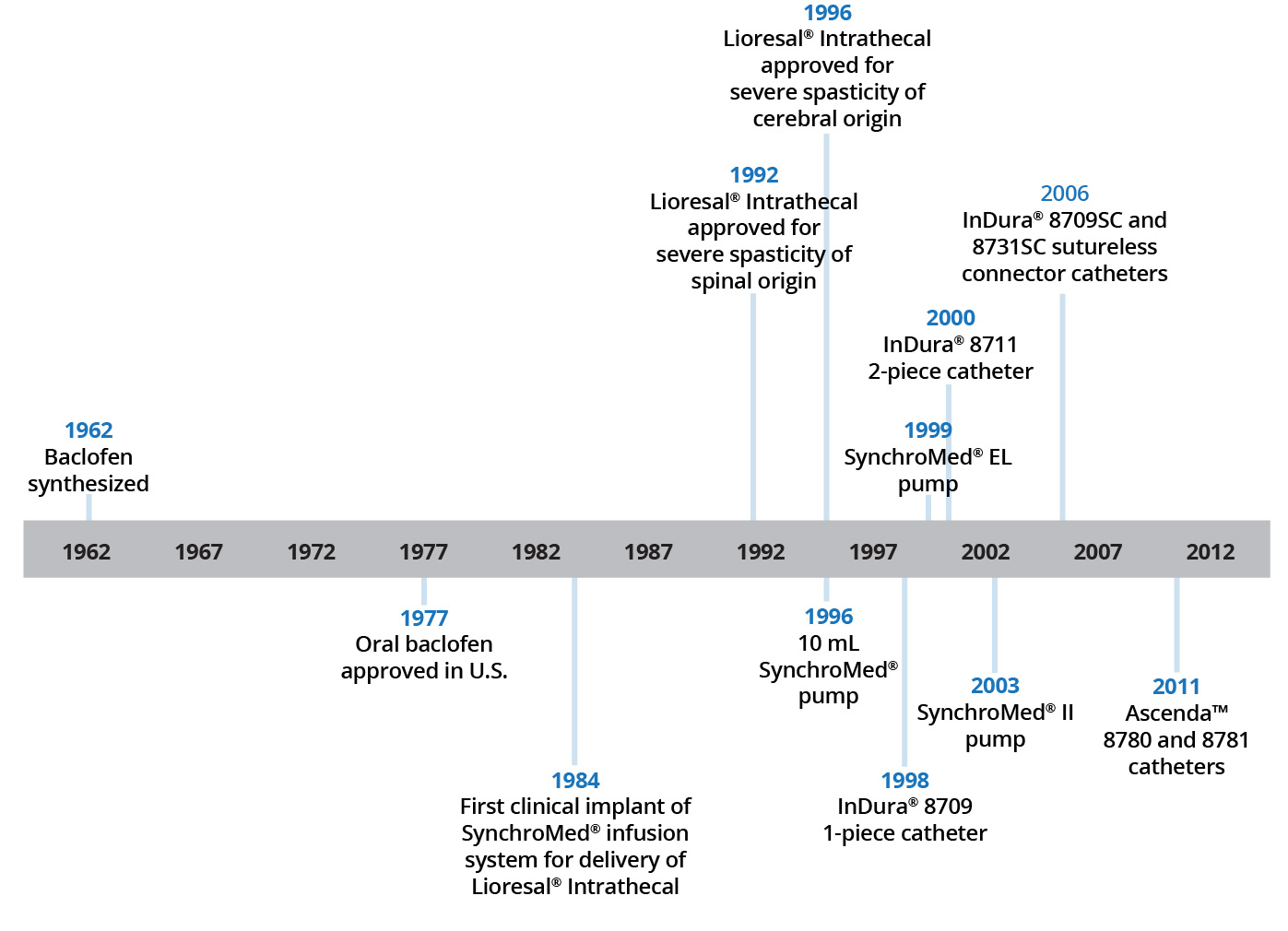
Source: Medtronic ITB Compendium

Prior to implantation of a device for chronic intrathecal infusion of Lioresal® Intrathecal, patients must show a response to Lioresal® Intrathecal in a screening trial. Implantation of the infusion system is contraindicated if the patient is of insufficient body size, requires a pump implant deeper than 2.5 cm, or, in the presence of spinal anomalies or active infection.
Following pump implantation, and for each adjustment of the dosing rate of the pump and/or concentration of Lioresal® Intrathecal, the patient should be monitored closely until it is certain the patient’s response to the infusion is acceptable and reasonably stable. Reservoir refilling must be performed by fully trained and qualified personnel following the directions provided by the pump manufacturer. Extreme caution must be used when filling an FDA approved implantable pump, following strict aseptic technique and ensuring refill directly into the reservoir and not the catheter access port.
- Lioresal® Intrathecal (baclofen injection) for intrathecal injection [prescribing information]. Amneal Pharmaceuticals LLC, Bridgewater, Jersey; January 2022..
- Muller H, Zierski J, Dralle D, Krauss D, Mutschler E. Pharmacokinetics of intrathecal baclofen. Local-spinal therapy of spasticity. 1988:223-226.
- Francisco GE, Saulino M. Chapter 19: Intrathecal baclofen for spasticity. In: Brashear A, Elovic E, eds. Spasticity: Diagnosis and Management. 2nd ed. New York, NY: Demos Medical Publishing, LLC, 2016.
- Penn RD. Intrathecal baclofen for spasticity of spinal origin: seven years experience. J Neurosurg. 1992;77:236-240.
- Coffey RJ, Cahill D, Steers W, et al. Intrathecal baclofen for intractable spasticity of spinal origin: results of a long-term multi-center study. J Neurosurg. 1993;78:226-232.