Long-term Dosing
Lioresal® Intrathecal provides a stable dosage of medication day after day, month after month—something that is not possible with oral baclofen therapy.1
Levels of baclofen in the blood and CSF can be unsteady throughout the day (with peaks and troughs) when dosed orally. A more stable dose of baclofen in the body means that the frequency and severity of spasms can be more consistently controlled.1
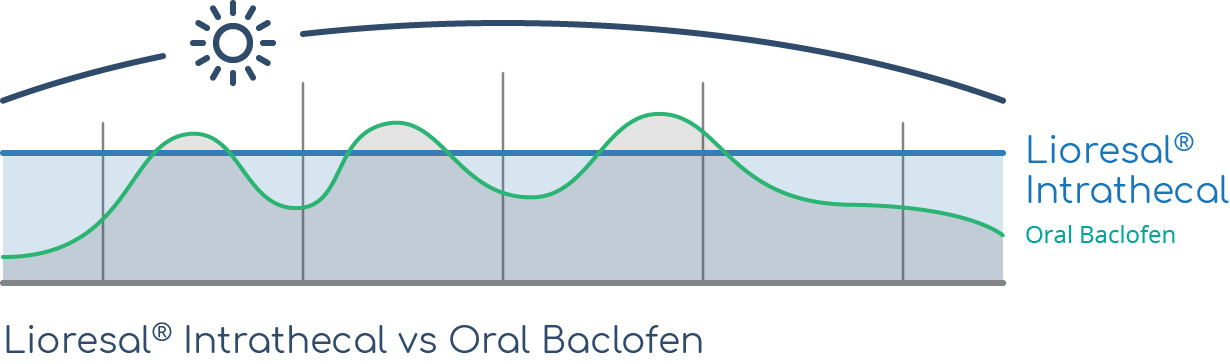
Many patients find that oral baclofen causes intolerable side effects, such as drowsiness.2 Oral baclofen can also produce inconsistent reduction in spasticity.2 Since patients have to take multiple pills throughout the day to achieve a therapeutic effect, the dose of baclofen working in the body over a 24-hour period is not consistent.3
Spasticity treatment with botulinum toxin, a focal spasticity treatment, is indicated for upper and lower limb spasticity. It takes effect 2 to 3 days after an injection, reaches peak therapeutic efficacy after 4 to 6 weeks, and then slowly wears off until it is no longer effective after 3 to 4 months.2,4 This method of treatment also leads to inconsistent management of spasticity.2
Due to the possibility of life-threatening CNS depression, cardiovascular collapse, and/or respiratory failure, physicians must be adequately trained and educated in chronic intrathecal infusion therapy.

- McCormick ZL, Chu SK, Binler D, et al. Intrathecal versus oral baclofen: a matched cohort study of spasticity, pain, sleep, fatigue, and quality of life. PM R. 2016;8(6):553-562.
- Saulino M, Ivanhoe CB, McGuire JR, et al. Best practices for intrathecal baclofen therapy: patient selection. Neuromodulation. 2016;19(6):607-615.
- KemstroTM (baclofen orally disintegrating tablets) for oral use [prescribing information]. Milwaukee, WI: Schwarz Pharma; Revised October 2003.
- Gracies JM, Brashear A, Jech R, et al. Safety and efficacy of abobotulinumtoxinA for hemiparesis in adults with upper limb spasticity after stroke or traumatic brain injury: a double-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14(10):992-1001.
- Lioresal® Intrathecal (baclofen injection) for intrathecal injection [prescribing information]. Saol Therapeutics, Roswell, Georgia; January 2019.